Now Reading: Building a Student Registration System: AI-Powered Class Diagram Creation with Visual Paradigm
-
01
Building a Student Registration System: AI-Powered Class Diagram Creation with Visual Paradigm
Building a Student Registration System: AI-Powered Class Diagram Creation with Visual Paradigm
Are you looking for a powerful AI-powered tool to transform your business requirements into a structured software design? Visual Paradigm‘s AI-Powered Textual Analysis Tool is a game-changer for developers, analysts, and architects. This feature allows you to generate a complete UML class diagram from a simple problem description, saving significant time and effort. This deep dive will guide you through the entire process of creating a class diagram for a “Student Registration System” using this innovative software.
Quick summary
-
Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Textual Analysis Tool automates the conversion of natural language into structured software design.
-
The process starts with a simple application name and proceeds through six intuitive steps.
-
The tool identifies candidate classes, details their attributes and operations, and defines relationships to generate a complete UML class diagram.
-
This AI-powered software is ideal for streamlining requirements analysis and accelerating the design phase of any software project.
Imagine you are tasked with designing a new system for a university. Your goal is to create a robust Student Registration System. Instead of spending hours manually analyzing requirements, you can use an AI-powered tool to generate a comprehensive design in minutes. The process begins with a simple input.
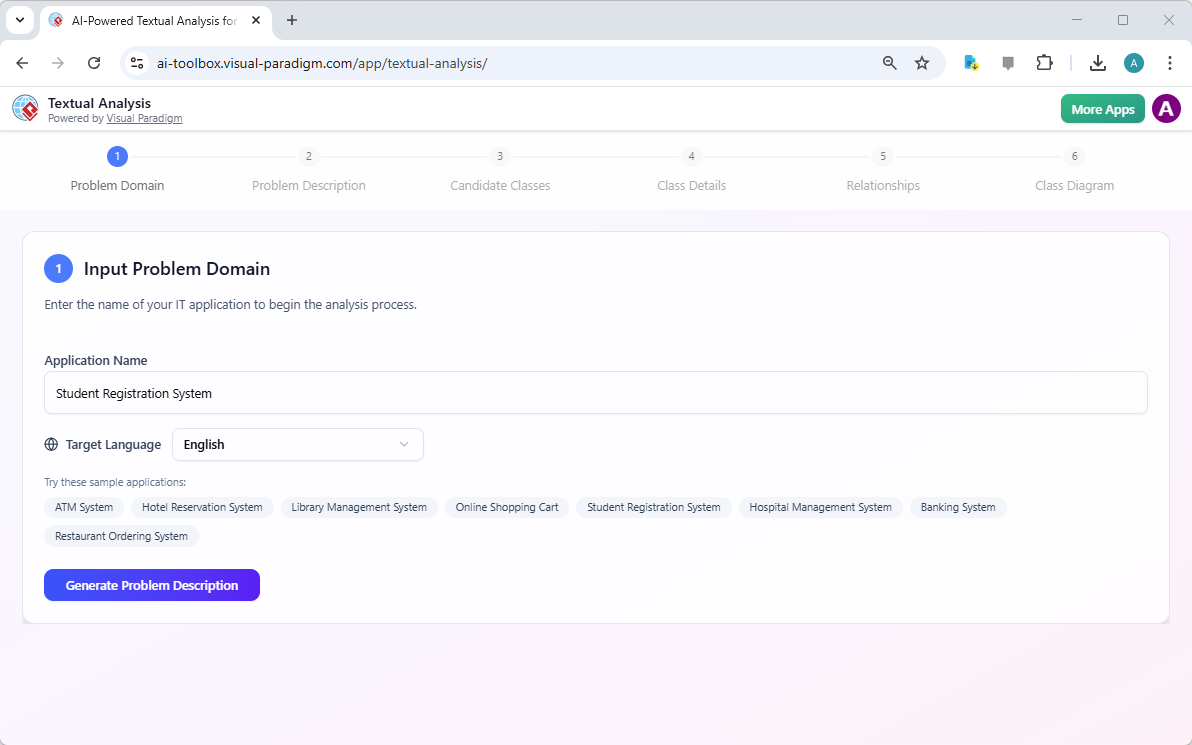
Step 1 is the “Input Problem Domain.” Here, you provide the name of your IT application. In this example, the user has entered “Student Registration System.” The tool also allows you to select the target language, with English being the default. After inputting the application name, the user clicks the “Generate Problem Description” button to move to the next stage.
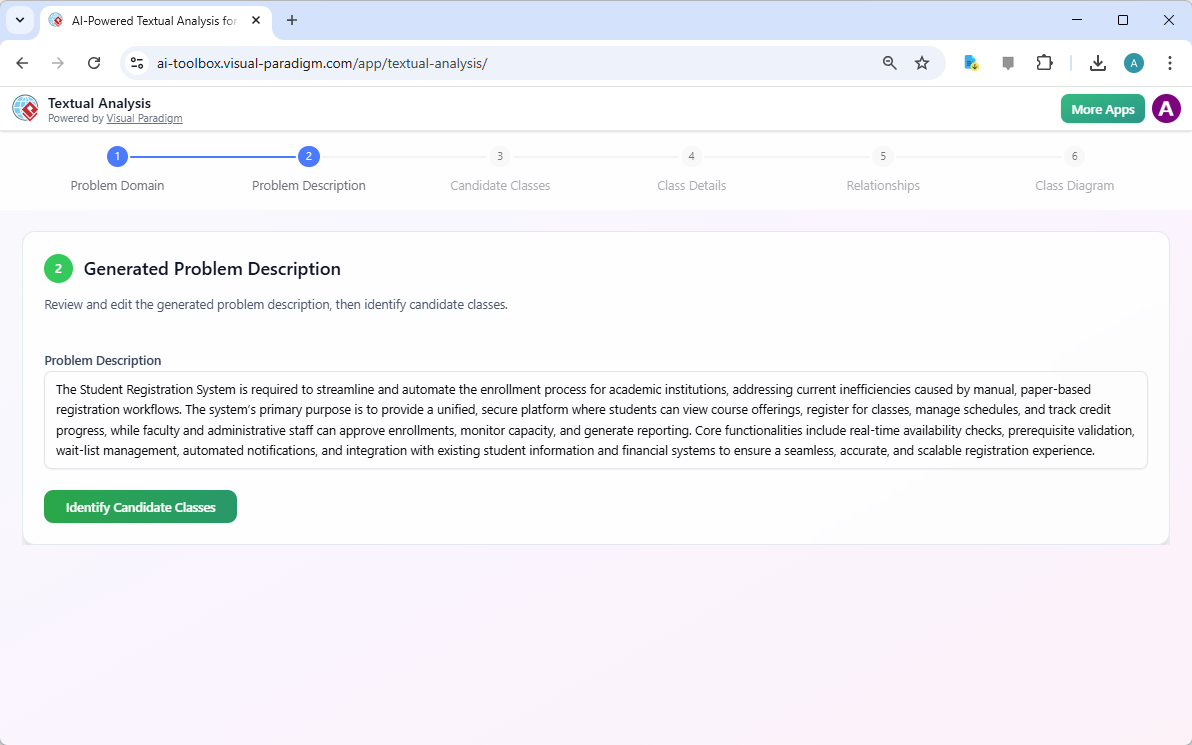
Step 2 is the “Generated Problem Description.” The AI analyzes the application name and generates a detailed narrative of the system’s purpose and core functionalities. This description acts as the foundation for the entire design process. It outlines the need to streamline the enrollment process, automate workflows, and provide a unified platform for students and staff. The AI identifies key requirements such as real-time availability checks, prerequisite validation, and integration with existing systems. This step is crucial as it ensures the subsequent analysis is grounded in a clear understanding of the problem domain.
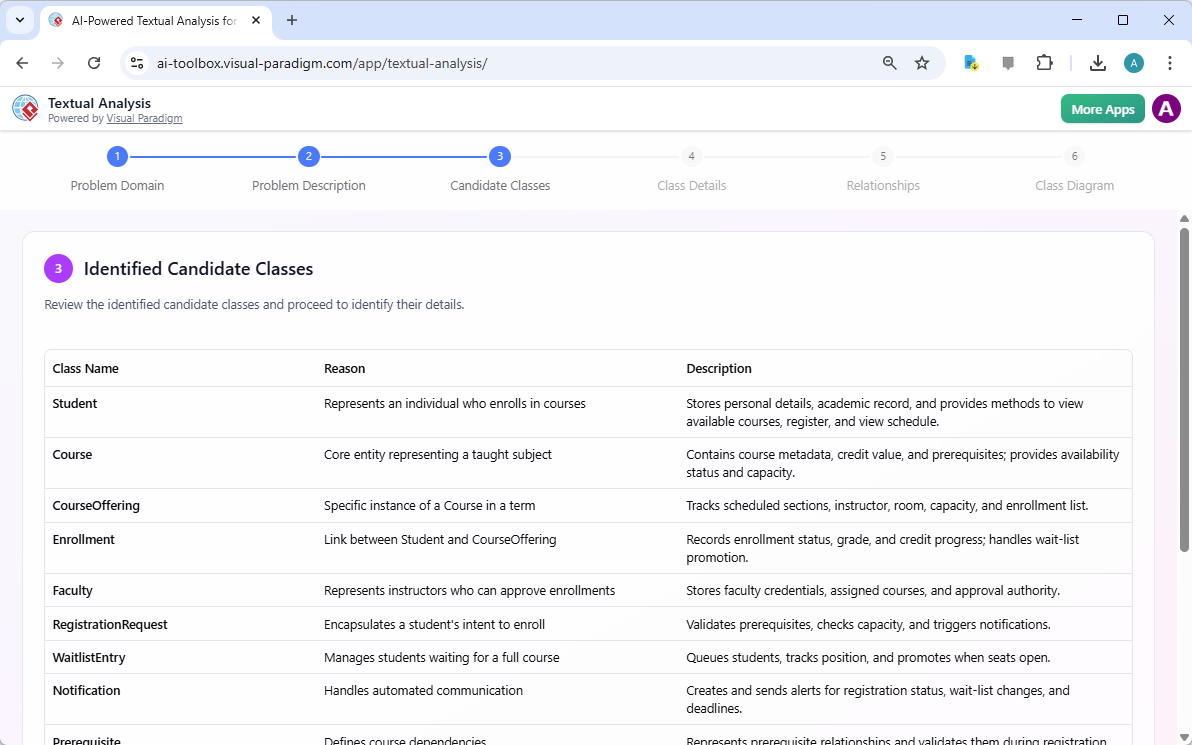
Step 3 is the “Identified Candidate Classes.” The AI takes the problem description and extracts potential classes from the text. It analyzes the nouns and phrases to identify the main entities within the system. The tool presents a list of these candidate classes, such as Student, Course, CourseOffering, Enrollment, Faculty, and RegistrationRequest. For each class, the AI provides a reason for its inclusion and a description of its role. For instance, the “Student” class is identified as an individual who enrolls in courses, while “CourseOffering” is a specific instance of a course in a term. This step is where the raw text is transformed into the building blocks of a structured design.
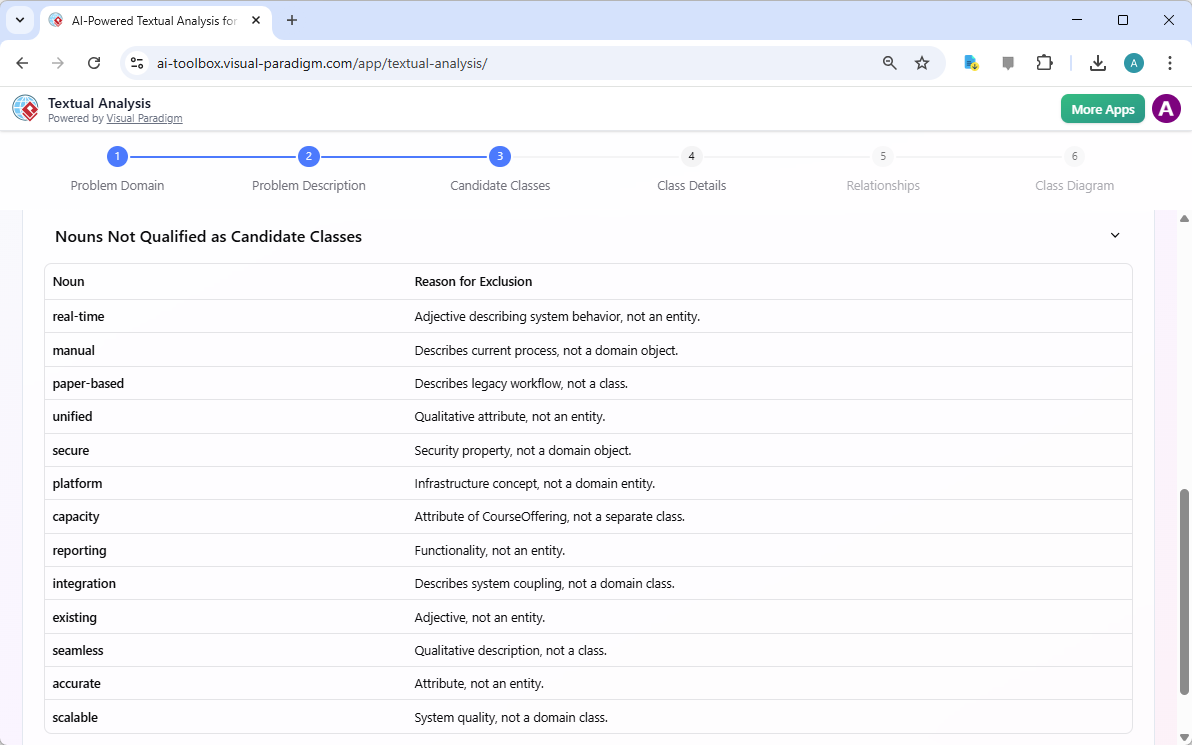
Step 3 continues with a critical refinement process. The AI also identifies nouns that are not suitable as candidate classes, such as “real-time,” “manual,” “paper-based,” “secure,” and “scalable.” These are excluded because they describe system properties, attributes, or behaviors rather than domain entities. This filtering step is essential for creating a clean and accurate model. It prevents the inclusion of non-essential elements and ensures the class diagram represents the core domain objects.
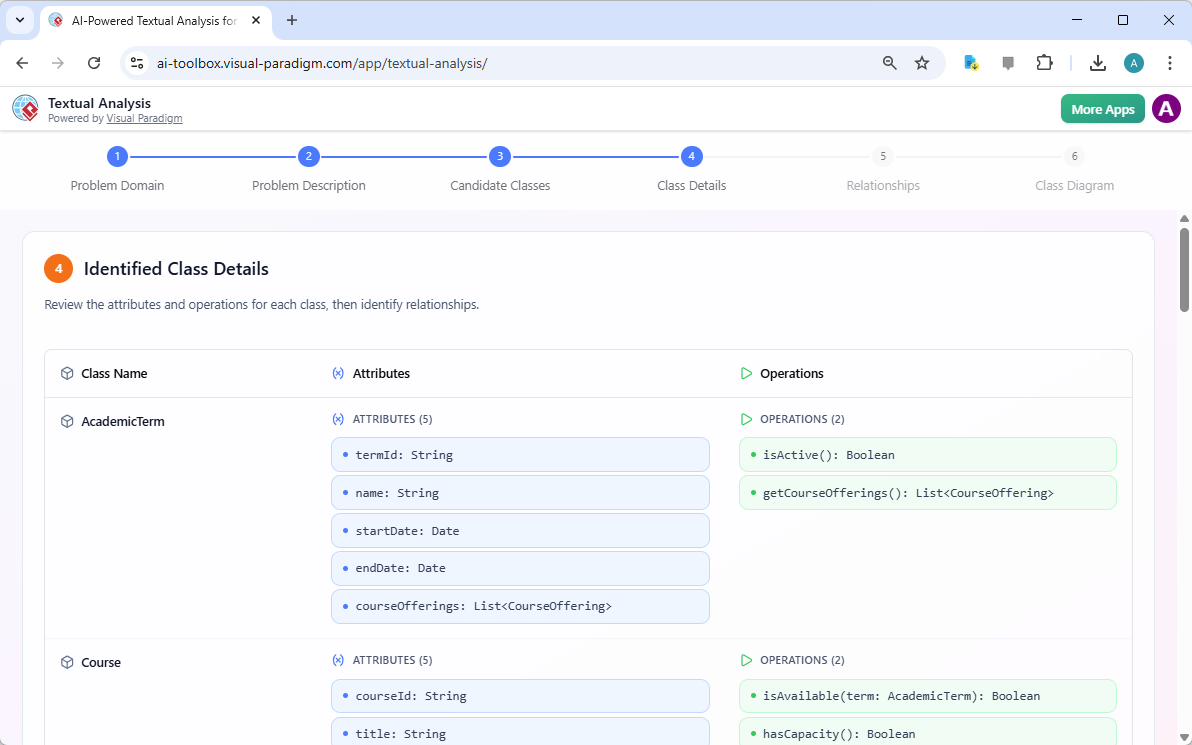
Step 4 is “Identified Class Details.” Now that the candidate classes are established, the AI delves deeper to define their structure. For each class, it identifies attributes (data) and operations (functions). For example, the “AcademicTerm” class is shown to have attributes like “termId,” “name,” “startDate,” and “endDate,” along with operations like “isActive()” and “getCourseOfferings().” Similarly, the “Course” class is defined with attributes like “courseId,” “title,” and “creditHours.” This detailed analysis provides the necessary information to create a fully functional and well-structured class diagram.
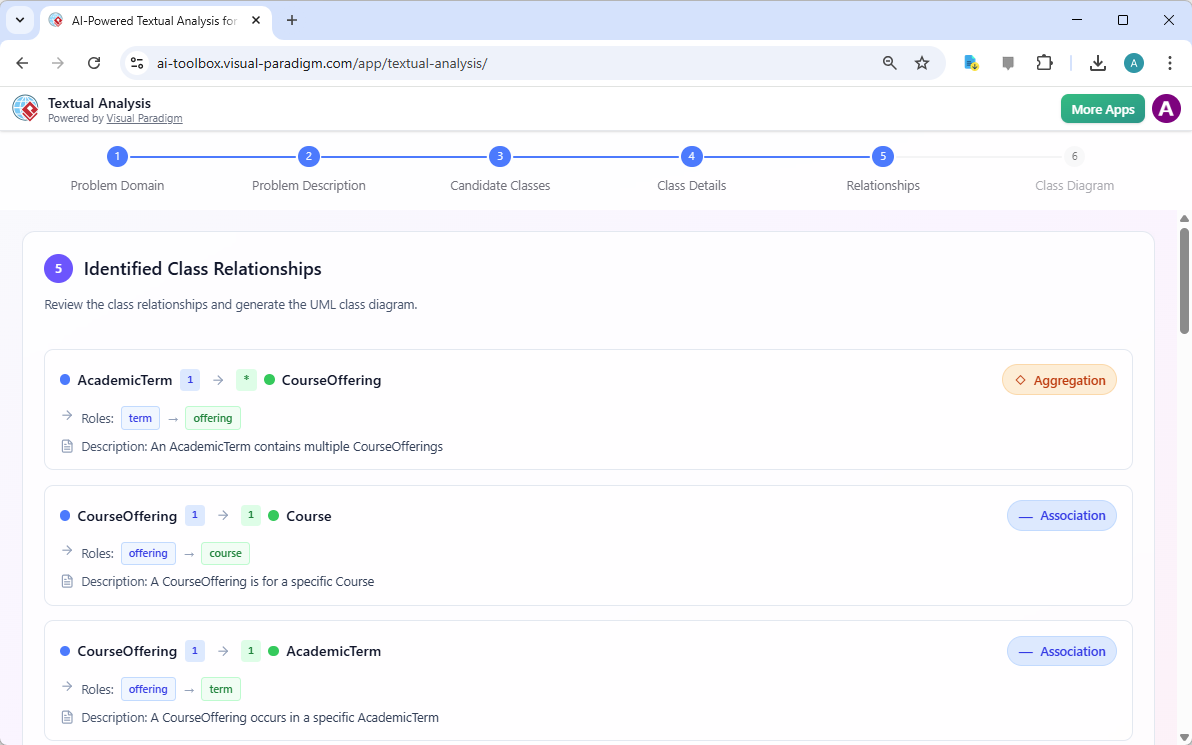
Step 5 focuses on “Identified Class Relationships.” The AI analyzes the interactions between the classes to define their connections. It identifies relationships such as aggregation and association. For instance, an “AcademicTerm” aggregates “CourseOffering,” meaning a term contains multiple course offerings. A “CourseOffering” is associated with a “Course” and an “AcademicTerm,” indicating that a specific offering is for a particular course during a specific term. These relationships are the glue that holds the system together, defining how the different components interact.
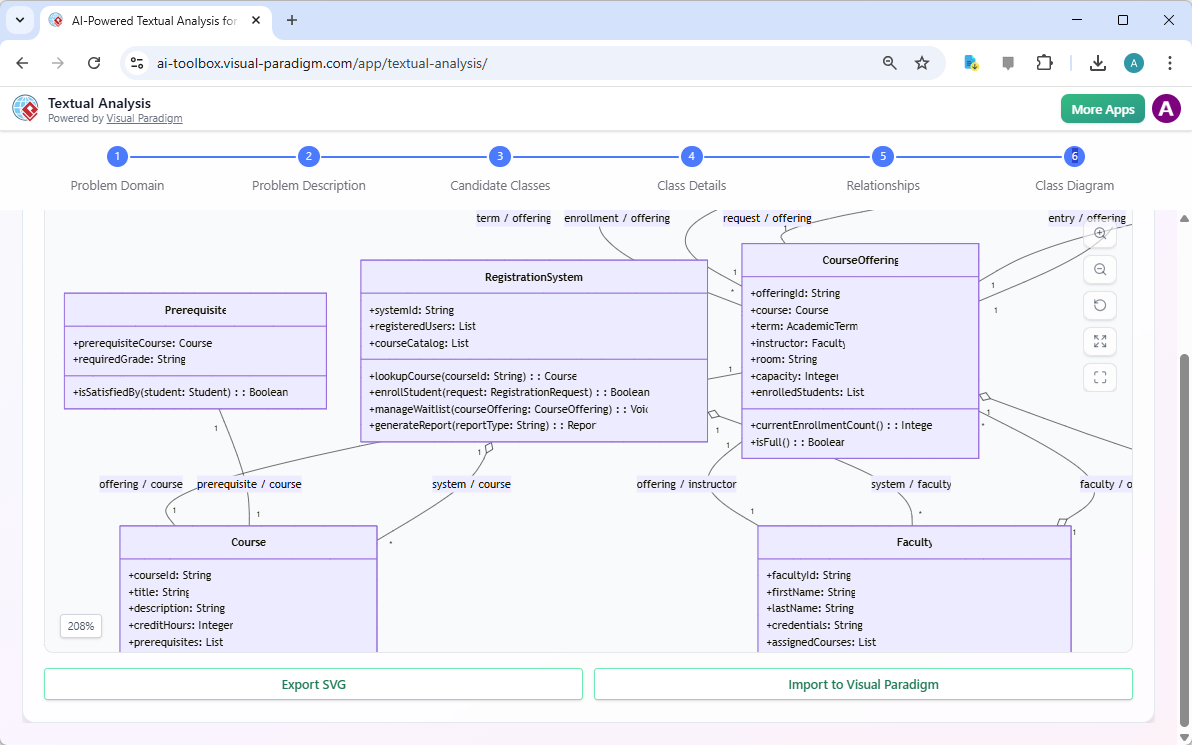
Step 6 is the final output: the “Class Diagram.” After all the analysis and refinement, the AI generates a complete, visual UML class diagram. The diagram displays all the classes, their attributes, operations, and the relationships between them. You can see the “RegistrationSystem” class at the center, with its operations like “lookupCourse” and “enrollStudent.” The diagram is fully interactive and can be exported as an SVG file or imported directly into Visual Paradigm for further development. This powerful AI-powered tool turns a simple text description into a professional, ready-to-use design artifact, significantly accelerating the software development lifecycle.
Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Textual Analysis Tool is a powerful solution for anyone involved in software design and requirements engineering. It leverages artificial intelligence to automate the complex process of transforming natural language into a structured UML class diagram. By following the six intuitive steps—Input Problem Domain, Generate Problem Description, Identify Candidate Classes, Refine Classes, Define Class Details, and Generate Relationships—you can quickly and accurately create a comprehensive design for your application. This AI-powered software is an invaluable asset for developers, analysts, and architects, allowing them to focus on innovation rather than tedious manual analysis.
Ready to streamline your software design process? Try the AI-Powered Textual Analysis Tool today. Download Visual Paradigm and experience the power of AI in your next project.
Related Links
Textual analysis tools in Visual Paradigm bridge the gap between unstructured information and formal design by transforming written descriptions into structured visual models. These tools utilize AI-driven processing to identify key entities, relationships, and candidate patterns, which significantly accelerates requirements engineering and software design workflows.
-
AI Textual Analysis – Transform Text into Visual Models Automatically: This feature leverages AI to analyze text documents and automatically generate UML, BPMN, and ERD diagrams, facilitating faster documentation and modeling.
-
AI-Powered Textual Analysis: From Problem Description to Class Diagram: A specialized guide focused on converting natural language problem descriptions into accurate, production-ready class diagrams.
-
Textual Analysis in Visual Paradigm: From Text to Diagram: An official documentation resource detailing the transition from written narratives to structured use case and class diagrams.
-
Visual Paradigm Textual Analysis Tool Features: An overview of the tool’s capabilities in deriving meaningful insights from large volumes of unstructured text through natural language processing.
-
Documenting Requirements Using Textual Analysis: This guide explains how to extract and organize requirements from project documents to enhance traceability and clarity across the development lifecycle.
-
Advanced Textual Analysis Techniques in Visual Paradigm: Explore sophisticated methods for text mining, including sentiment analysis and keyword extraction, to gain deeper analytical insights.
-
What is Textual Analysis? – Visual Paradigm Circle: An introductory resource covering the purpose and strategic benefits of implementing textual analysis within standard project workflows.
-
Identifying Domain Classes Using AI Textual Analysis: A tutorial on streamlining domain modeling by using AI to automatically identify and categorize potential classes directly from text.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Toolbox: Textual Analysis for Software Modeling: A web-based application within the AI Toolbox that allows users to identify entities and concepts to build structured software models from unstructured input.
-
Case Study: AI-Powered Textual Analysis for UML Class Diagram Generation: A real-world evaluation demonstrating how AI-driven extraction improves the accuracy and efficiency of generating models from complex requirements.












