Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI: From Natural Language to Production-Ready SQL
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI: From Natural Language to Production-Ready SQL
Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI: From Natural Language to Production-Ready SQL
Empower Your Database Design with AI-Powered Intelligence
🎯 Introduction: Revolutionizing Database Design with AI
In the fast-paced world of software development, designing a robust, scalable, and maintainable database is foundational to building reliable applications. Traditionally, this process involved multiple time-consuming steps: gathering requirements, creating conceptual models, refining logical designs, normalizing schemas, validating constraints, and testing with real data.
Enter Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI — a groundbreaking, browser-based AI tool that transforms natural language descriptions into fully normalized, production-ready SQL schemas in minutes.
✅ No more guesswork. No more manual modeling errors. Just intelligent, guided database design.
Built as part of Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered ecosystem, DB Modeler AI is not just another diagramming tool. It’s a smart, educational, and interactive workflow engine designed for developers, architects, students, and teams who want to accelerate their database design process without sacrificing quality or control.
🔗 Quick Access
🚀 Launch DB Modeler AI Now:
👉 https://ai-toolbox.visual-paradigm.com/app/dbmodeler-ai/
🧭 The 7-Step AI-Guided Workflow: A GPS for Database Design
DB Modeler AI follows a structured, linear, and interactive 7-step workflow, ensuring no critical step is skipped. Each phase builds on the last, with AI assistance and real-time user input, making it ideal for learning, prototyping, and enterprise-grade development.
Let’s walk through each step in detail.
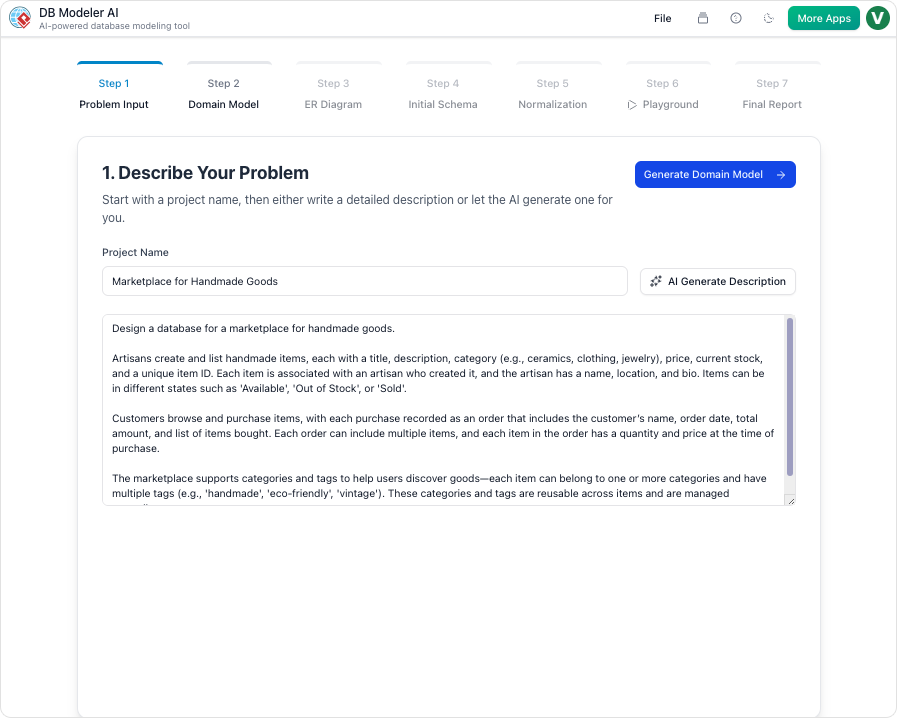
✅ Step 1: Problem Input – Describe Your System in Plain English
“Tell me what your app does — in your own words.”
This is where the journey begins. You provide:
-
A project name (e.g., “Online Bookstore”)
-
A natural language description of your system (e.g., “An online bookstore to manage books, customers, orders, inventory, authors, and reviews, including tracking stock levels and customer wishlists.”)
🤖 AI Expansion (Smart Enhancement)
If your input is brief or vague, the AI automatically expands it by:
-
Identifying core business entities
-
Inferring relationships and cardinalities
-
Extracting business rules (e.g., “Each order must have at least one item”, “A book can have multiple authors”)
💡 Pro Tip: Be specific! Include constraints, workflows, and user interactions. The richer the description, the better the initial model.
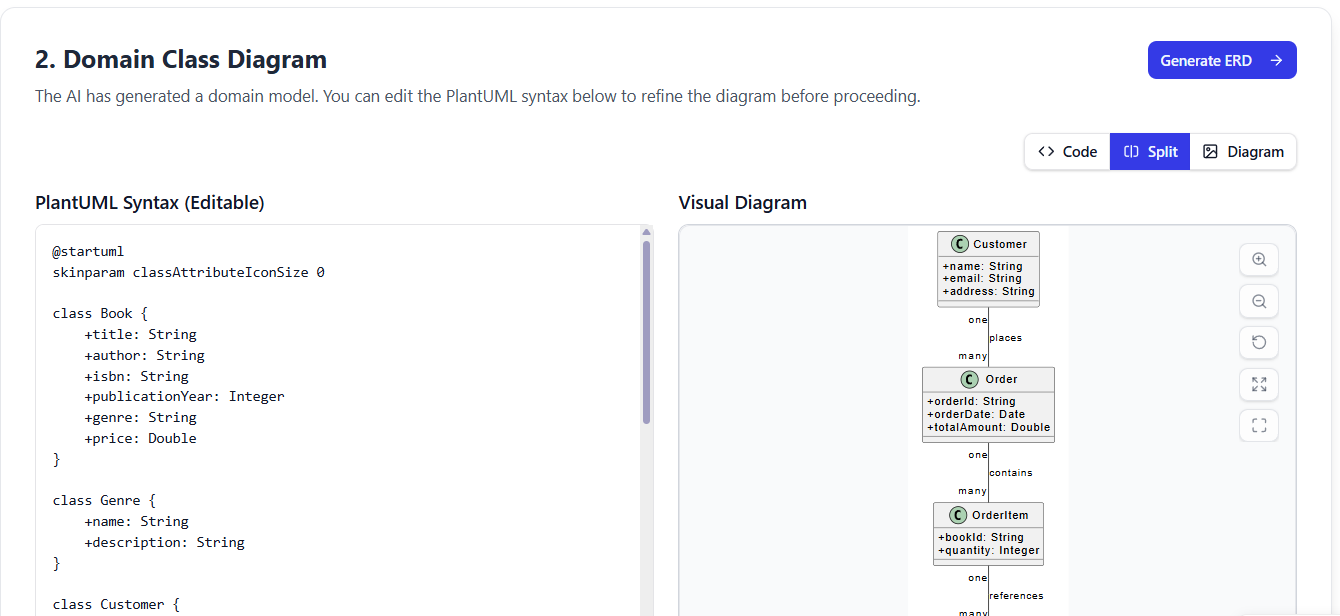
✅ Step 2: Domain Class Diagram (Conceptual Modeling)
“What are the key concepts in your business?”
The AI generates a high-level Domain Class Diagram using PlantUML syntax, focusing on business semantics, not technical details.
📌 Example Output (Simplified):
@startuml
class Book {
- title: String
- isbn: String
- price: Decimal
- publishDate: Date
}
class Customer {
- name: String
- email: String
- address: String
}
class Order {
- orderDate: DateTime
- status: String
}
Customer "1" -- "0..*" Order
Book "1" -- "0..*" Order
Book "1" -- "0..*" Review
@enduml
🔧 Interactive Editing
-
Edit the PlantUML code directly in the editor.
-
Use the AI Chatbot to refine the model:
-
“Add a payment status field to Order.”
-
“Make the relationship between Author and Book many-to-many.”
-
“Add a wishlist entity that links customers and books.”
-
✅ This step ensures alignment with business logic before moving to technical modeling.
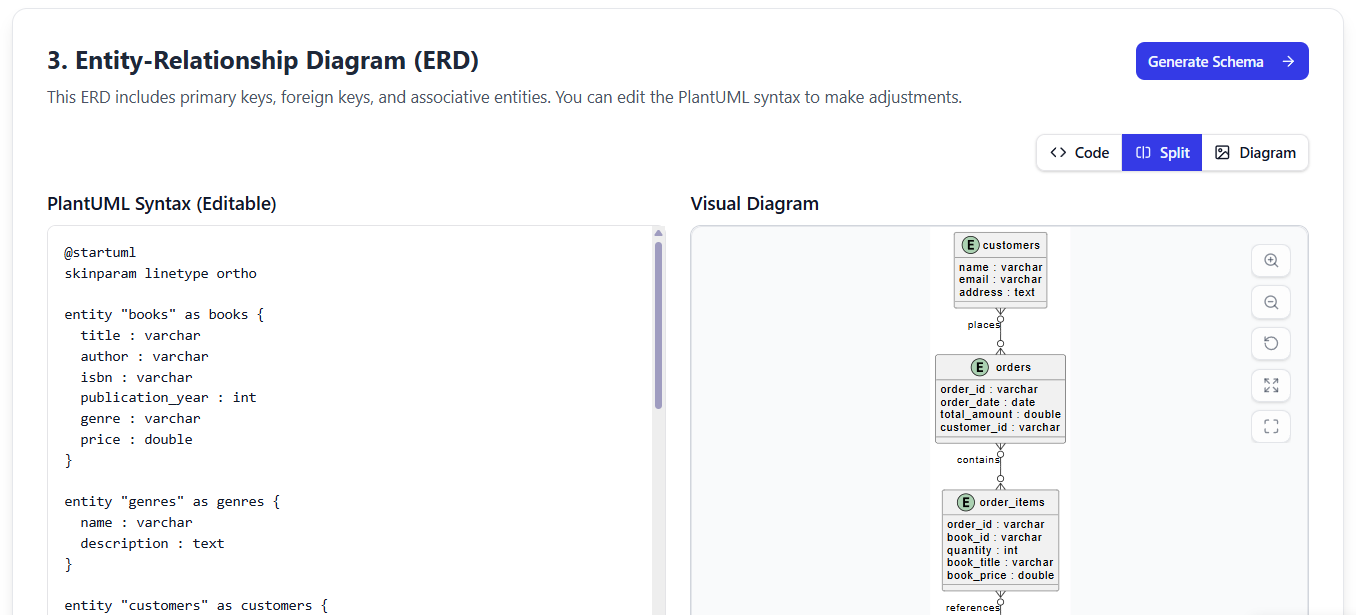
✅ Step 3: ER Diagram (Logical Modeling)
“Now, let’s turn concepts into a relational structure.”
The tool automatically converts your domain model into a fully detailed Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD), complete with:
-
Primary Keys (PKs) assigned to each entity
-
Foreign Keys (FKs) for relationships
-
Cardinalities (1:1, 1:N, M:N) clearly labeled
-
Junction tables created for many-to-many relationships
🎯 Key Features:
-
Drag-and-drop layout for clean, readable diagrams
-
Click to edit attributes, relationships, or constraints
-
AI suggests optimal relationships based on semantics
🛠 Example:
Order→OrderItem(M:N) →BookbecomesOrder–OrderItem–Bookwith proper FKs.
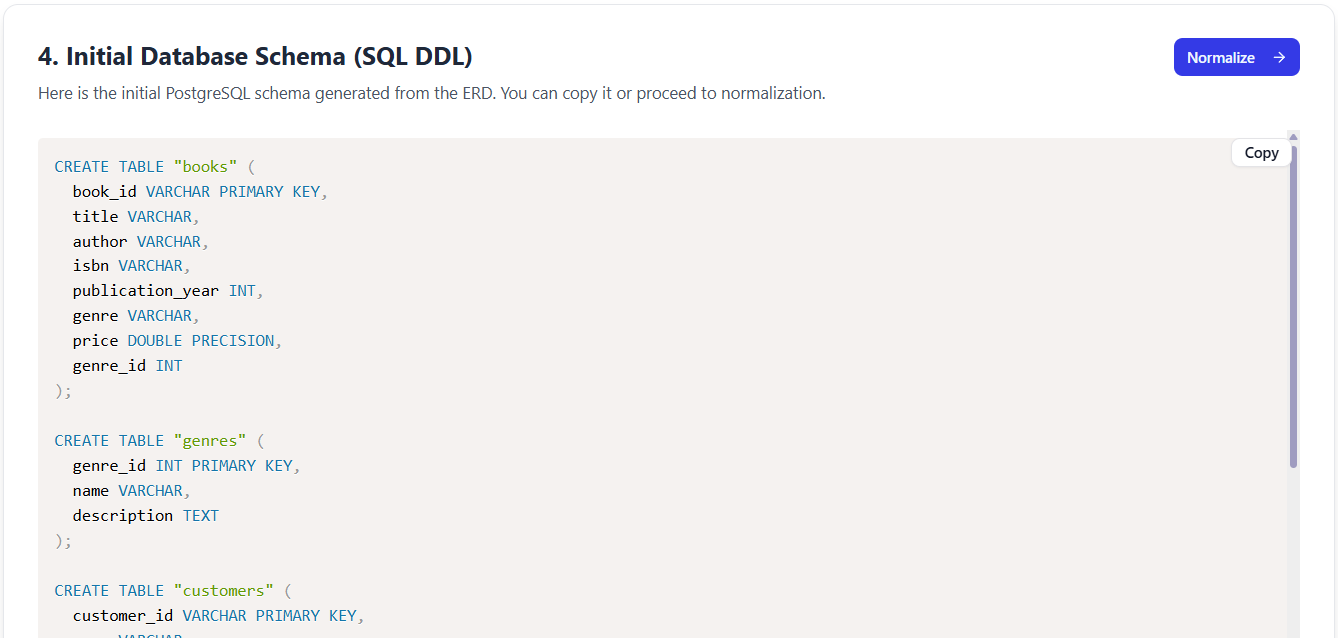
✅ Step 4: Initial Schema Generation (SQL DDL)
“Time to generate the actual database schema!”
Your ERD is now converted into executable SQL DDL (Data Definition Language) code, compatible with PostgreSQL, with intelligent defaults.
📥 Sample Output (Partial):
CREATE TABLE "book" (
"id" UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
"title" VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
"isbn" VARCHAR(13) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
"price" DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
"publish_date" DATE,
"created_at" TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE "customer" (
"id" UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
"name" VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
"email" VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
"address" TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE "order" (
"id" UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
"customer_id" UUID NOT NULL REFERENCES "customer"("id"),
"order_date" TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
"status" VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'Pending'
);
🔍 Review Tips:
-
Double-check data types: Use
DECIMAL(10,2)for money,VARCHAR(n)for strings -
Ensure
NOT NULLconstraints match business rules -
Add indexes on frequently queried fields (e.g.,
customer_id,isbn)
✅ The AI makes smart suggestions, but your domain knowledge is key.
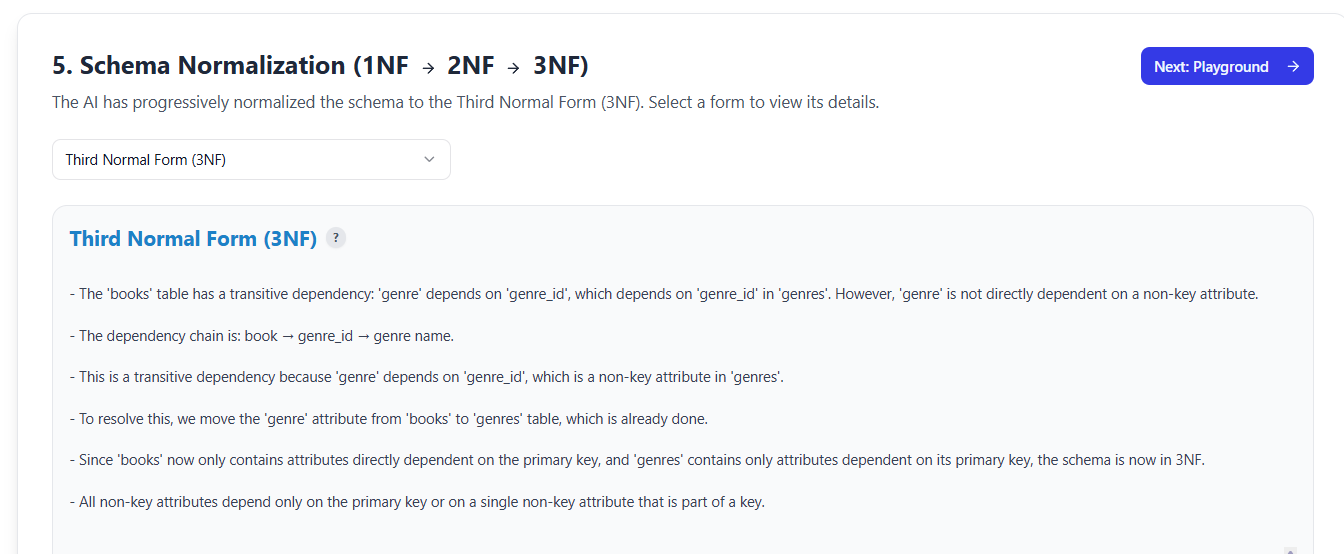
✅ Step 5: Intelligent Normalization (3NF Optimization)
“Let’s eliminate redundancy and anomalies!”
This is where DB Modeler AI shines. The tool doesn’t just generate a schema — it intelligently normalizes it to 3NF (Third Normal Form) with clear, educational feedback.
🔄 Step-by-Step Process:
-
1NF: Ensures atomic values (no repeating groups)
-
2NF: Removes partial dependencies (non-key attributes depend on full PK)
-
3NF: Removes transitive dependencies (non-key attributes depend only on PK)
📌 Example Explanation from AI:
✅ “Splitting the ‘order_item’ table into ‘order’ and ‘order_item’ eliminates update anomalies. The quantity and price were transitively dependent on order_id, not the composite key.”
✅ Result: A clean, normalized schema free from insertion, deletion, and update anomalies.
📚 This step is educational — perfect for students and junior developers learning database theory.
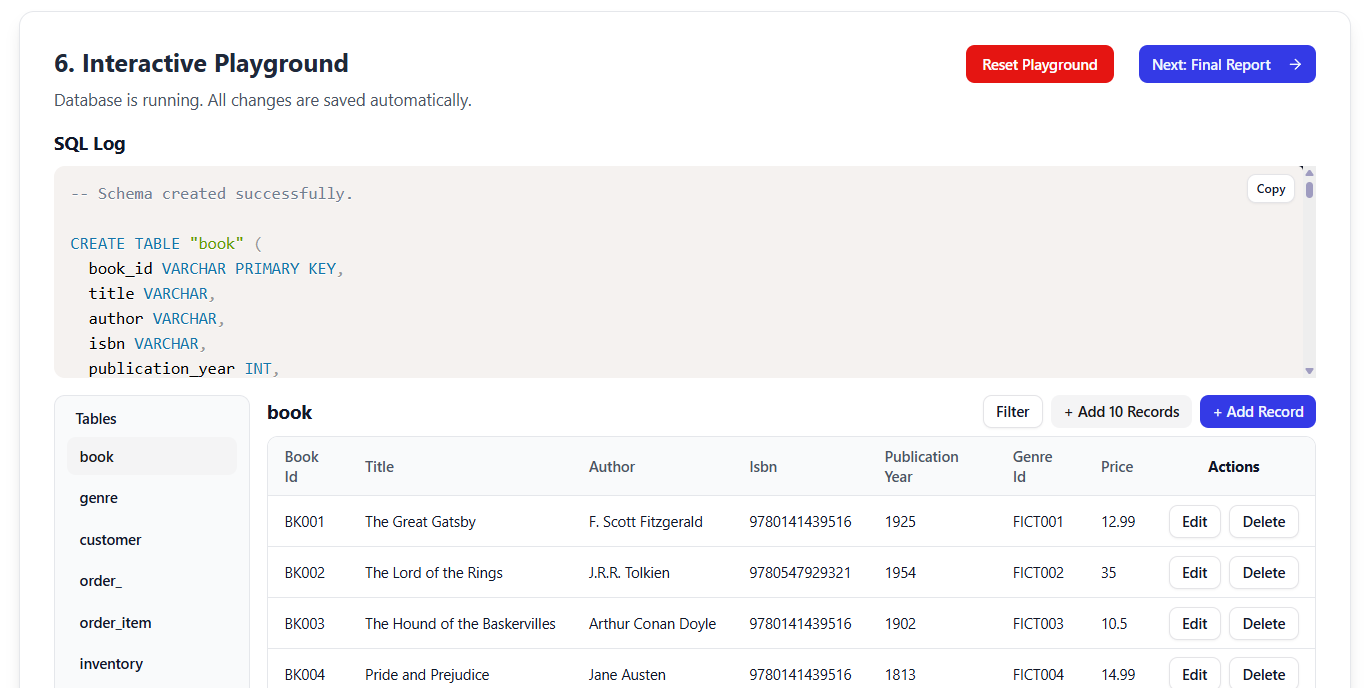
✅ Step 6: Interactive Playground (Live SQL Sandbox)
“Test your schema — live, in your browser!”
No database setup required. The AI generates realistic sample data (DML) and provides a full in-browser SQL client.
🧪 Features:
-
Auto-generated inserts for all tables (e.g., 5 sample books, 3 customers, 2 orders)
-
Run CRUD operations and complex queries:
SELECT c.name, b.title, o.order_date FROM customer c JOIN "order" o ON c.id = o.customer_id JOIN order_item oi ON o.id = oi.order_id JOIN book b ON oi.book_id = b.id WHERE o.status = 'Shipped'; -
Real-time feedback: See results instantly
-
Validate that your schema supports real-world use cases
🔍 If joins are too complex or performance is poor → Go back to Step 3 and refine the ERD.
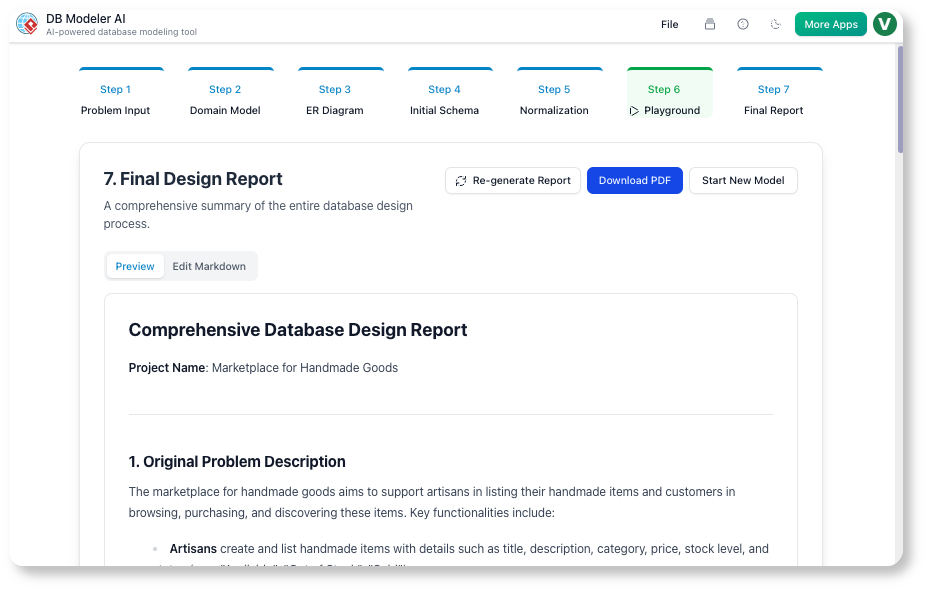
✅ Step 7: Final Report & Export
“Compile everything into professional documentation.”
The final step delivers a complete, shareable package of your database design.
📄 What’s Included:
-
Original problem description
-
Domain Class Diagram (PlantUML)
-
Final ER Diagram (visual)
-
Final SQL DDL (ready to deploy)
-
Sample DML inserts (for testing)
-
Normalization rationale (why changes were made)
-
Example queries demonstrating functionality
📥 Export Options:
| Format | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Share with team, submit for grading | |
| Markdown | Integrate into documentation, GitHub README |
| JSON Project File | Import into Visual Paradigm Desktop (Pro+) for advanced features |
🔄 Integration Bonus: Import the JSON into Visual Paradigm Desktop for:
-
Reverse engineering
-
Code generation (Java, C#, Python)
-
Round-trip engineering
-
UML/BPMN integration
🛠️ Key Features at a Glance
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Natural Language to DDL | Turn simple prompts into full SQL schema in minutes |
| PlantUML-Based Editing | Edit models in text format — version control friendly |
| Live SQL Sandbox | Test queries instantly — no setup needed |
| AI-Powered Normalization | Auto-optimizes to 3NF with clear explanations |
| Desktop Sync (JSON Export) | Seamless handoff to Visual Paradigm Desktop |
| AI Chatbot Assistance | Refine models iteratively (“Add user authentication”) |
| Browser-Based & Cross-Platform | Works on Mac, Windows, Linux, tablets — no install |
💡 Pro Tips for Maximum Impact
-
Iterate Early & Often
Refine your Domain Class Diagram and ERD in Steps 2–3 using the AI chatbot. Small changes now prevent costly rework later. -
Validate Data Types & Constraints
AI is smart, but you know your domain best. Double-check:-
DECIMAL(10,2)for money -
VARCHAR(255)for emails -
NOT NULLon critical fields
-
-
Leverage the Playground
Simulate real queries your app will run. If performance is poor, consider selective denormalization (only if justified). -
Start Simple
Test with familiar domains:-
Online bookstore
-
Hospital management system
-
Task tracker app
-
E-commerce platform
-
-
Combine with Other VP Tools
Use generated artifacts in:-
Visual Paradigm Online (UML modeling)
-
Visual Paradigm Desktop (code generation, reverse engineering)
-
Use Case Modeling Studio (for full system design)
-
📌 Want a Worked Example? Let’s Build a Bookstore!
🔹 Prompt:
“Create an online bookstore system that allows customers to browse books, place orders, leave reviews, and manage wishlists. Authors can write multiple books, and books can have multiple authors. Track stock levels, order status, and customer preferences.”
✅ Expected Output Structure:
-
Problem Input: Expanded description with entities, relationships, and rules
-
Domain Class Diagram: PlantUML with
Book,Customer,Order,Review,Author,Wishlist,OrderItem -
ER Diagram: With PKs, FKs, M:N relationships resolved via junction tables
-
SQL DDL: PostgreSQL-compatible
CREATE TABLEstatements -
Normalization Report: Step-by-step explanation of 1NF → 3NF transitions
-
Interactive Playground: Sample data + queries like:
-
“List all books with their average review rating”
-
“Find customers who have ordered more than 3 books”
-
-
Final Export: PDF or Markdown report ready for documentation
🏁 Conclusion: Build Faster, Design Smarter
Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI is not just a tool — it’s a digital co-pilot for database architects and developers. By combining natural language understanding, AI-guided normalization, interactive testing, and professional documentation, it transforms database design from a tedious chore into a fast, fun, and educational experience.
Whether you’re:
-
A student learning database design
-
A developer prototyping a new app
-
A team lead ensuring consistency across projects
-
Or a teacher demonstrating real-world modeling
👉 DB Modeler AI delivers faster time-to-deployment, fewer errors, and higher-quality databases — all from a simple prompt.
📣 Ready to Get Started?
🚀 Launch DB Modeler AI Now:
👉 https://ai-toolbox.visual-paradigm.com/app/dbmodeler-ai/
📚 Further Reading & Resources
✉️ Have feedback? Reach out to the Visual Paradigm community or join the AI-powered design revolution today!
✨ Design with Intelligence. Build with Confidence.
Visual Paradigm DB Modeler AI – Your AI-Powered Database Design Partner.
Resource
- Visual Paradigm ERD Tool – Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams Online: This powerful, web-based ERD tool allows users to design and visualize database schemas using intuitive drag-and-drop features.
- Database Design with ERD Tools – Visual Paradigm Guide: a comprehensive guide focused on using ERD tools to design robust, scalable databases through best practices in data modeling and schema design.
- Generating Database from ERD in Visual Paradigm: This documentation provides detailed instructions on automatically generating a database schema directly from an ERD using reverse engineering capabilities.
- How to Create Database Specifications in Visual Paradigm: A step-by-step tutorial on creating database specifications, an essential task for professional database design and modeling.
- Comprehensive Guide to Visual Paradigm AI Table Generator: This guide explores transforming natural language descriptions into fully functional database tables and executable code via an advanced AI engine.
- Why Visual Paradigm Online is Ideal for ERD Design in Development Teams: A case study illustrating how the online platform supports collaboration and real-time editing for agile development teams during ERD design.
- Streamlining Entity-Relationship Modeling with Visual Paradigm: This resource explains how to simplify the process of designing and implementing ER models from the initial concept to final database deployment.
- Reverse Engineering Database to ERD in Visual Paradigm: A guide on how to reverse engineer an existing database into an ERD using an intuitive interface and powerful modeling tools.
- The Comprehensive Guide to DBModeler AI: This guide covers how the AI-powered DBModeler combines expert guidance with visual diagramming and live SQL testing for modern database design.
- AI-Powered Database Modeling with DBModeler AI: An introduction to how DBModeler AI facilitates intelligent database schema design and automated modeling within the Visual Paradigm ecosystem.