Now Reading: Comprehensive Tutorial on UML State Machine Diagrams: From Fundamentals to AI-Powered Development (2026)
-
01
Comprehensive Tutorial on UML State Machine Diagrams: From Fundamentals to AI-Powered Development (2026)
Comprehensive Tutorial on UML State Machine Diagrams: From Fundamentals to AI-Powered Development (2026)
Master Behavior Modeling with Real-World Examples, Best Practices, and Visual Paradigm’s AI Generator
1. What Is a State Machine Diagram? (The Core Concept)
A UML State Machine Diagram (also known as a Statechart or State Diagram) is a visual representation of the dynamic behavior of a system or object over time.
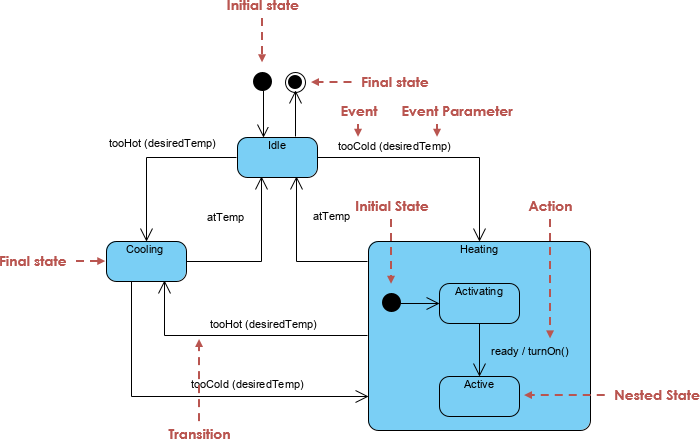
It models:
-
States – the condition or situation an object is in
-
Transitions – changes from one state to another
-
Events – triggers that cause transitions
-
Guards – conditions that must be true for a transition to occur
-
Actions – operations performed during a transition or state entry/exit
🎯 Purpose: To capture complex behavior in a clear, standardized way — especially when systems involve event-driven logic, concurrent operations, or lifecycle changes.
📌 Standard: UML 2.5 (officially defined by the Object Management Group – OMG)
2. Key Elements & Notations (The Language of State Machines)
Understanding these building blocks is essential for reading and creating accurate diagrams.
| Element | Symbol | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| State | Rounded rectangle | A condition the system is in | LoggedIn, Processing, OutOfStock |
| Initial Pseudostate | Solid black circle | Start of the diagram | → from initial state |
| Final Pseudostate | Black circle inside white circle | End of the diagram | → to final state |
| Transition | Arrow with label | Event → State change | paymentReceived → Paid |
| Event | Text on arrow | What triggers the change | paymentReceived |
| Guard | [condition] in brackets |
Only trigger if condition is true | [stockAvailable] |
| Action | action after → |
What happens during transition | sendConfirmation() |
| Entry Action | entry: action |
Runs when entering a state | entry: logLogin() |
| Exit Action | exit: action |
Runs when leaving a state | exit: clearSession() |
| Composite State | Nested states inside a larger state | Sub-states within a parent | Processing → Shipping, Billing |
| Orthogonal Region | Parallel regions | Concurrent behaviors | Payment and Shipping running at once |
| History Pseudostate | H or Hs/Hd |
Return to last substate | shallow history (Hs) on Cancelled |
✅ Best Practice: Always label transitions as:
event [guard] → action
Example:paymentReceived [stockAvailable] → sendConfirmation()
3. When to Use a State Machine Diagram (Real-World Use Cases)
State machine diagrams are not just for theory — they’re critical in real-world systems where behavior evolves over time.
✅ Best Use Cases (2026)
| Industry/Domain | Use Case | Why State Machine? |
|---|---|---|
| E-Commerce | Order lifecycle: Created → Paid → Shipped → Delivered | Tracks complex transitions with guards and actions |
| Embedded Systems | Elevator control, traffic lights, IoT devices | Handles concurrency, timers, and failure states |
| Microservices | Payment gateway, order processing, authentication | Models event-driven workflows across services |
| User Interfaces (UI) | Form validation, navigation states, modal dialogs | Manages user interactions and state changes |
| Healthcare | Patient appointment workflow: Scheduled → Confirmed → InProgress → Completed | Tracks real-world processes with concurrency (e.g., payment & check-in) |
| Automotive | Vehicle state: Off → Idle → Driving → Parking → Sleep | Handles safety, diagnostics, and power management |
| Financial Systems | Transaction lifecycle: Pending → Approved → Settled → Failed | Enforces business rules via guards and actions |
🚨 Don’t use it for: Simple data structures or static workflows — use Activity Diagrams or Sequence Diagrams instead.
4. Step-by-Step: How to Create a State Machine Diagram (Beginner to Pro)
✅ Step 1: Identify the System & Its States
Ask:
“What are the main conditions the system can be in?”
👉 Example: For a user login system, states are: Logged Out, Logging In, Logged In, Locked Out.
✅ Step 2: List Events That Trigger Transitions
“What causes the system to change state?”
👉 Example: clickLogin, invalidPassword, timeout, logout
✅ Step 3: Define Transitions with Events, Guards & Actions
“When does the system move from one state to another?”
👉 Example:
clickLogin → Logged In
invalidPassword [attempts > 3] → Locked Out
✅ Step 4: Add Entry/Exit Actions
“What should happen when entering or leaving a state?”
👉 Example:
entry: logLoginAttempt() on Logging In
exit: clearSession() on Logged Out
✅ Step 5: Use Composite States & Orthogonal Regions (Advanced)
“Can multiple behaviors happen at once?”
👉 Example: A smart thermostat can be both Heating and AutoMode → use orthogonal regions.
✅ Step 6: Validate the Model
Ask the AI:
“Check for unreachable states, dead ends, or missing guards.”
5. Real-World Examples (With AI-Powered Generation)
🛒 Example 1: E-Commerce Order Lifecycle
Prompt to AI Generator:
“Generate a State Machine for an Order in an e-commerce system with states: Created, Pending Payment, Paid, Processing, Shipped, Delivered, Cancelled, Refunded. Include transitions triggered by paymentReceived, shipOrder, cancelOrder, and timeout. Add guards: [stockAvailable], [paymentValid]. Add entry actions: logOrderStart(), sendConfirmation(). Add shallow history on Cancelled.”
✅ Result: A clean, compliant UML 2.5 diagram with:
-
Initial/final states
-
Guards and actions
-
Shallow history
-
Orthogonal regions (if requested)
📌 Use Case: Ideal for backend developers, product managers, and QA teams.
🏗️ Example 2: Elevator Control System
Prompt:
“Generate a State Machine for an elevator: states Idle, MovingUp, MovingDown, DoorsOpening, DoorsOpen, DoorsClosing. Include floor requests, emergency stop with deep history, and a concurrent region for door and movement operations. Add entry action ‘playDing()’ on DoorsOpen and do activity ‘monitorSensors()’ in Moving states.”
✅ Result: A robust, concurrent model that handles real-world edge cases.
📌 Use Case: Perfect for embedded systems, robotics, and safety-critical software.
🍭 Example 3: Vending Machine
Prompt:
“Generate a state machine for a vending machine: states Idle, Selecting, Paid, Dispensing, OutOfStock. Include coin insert, selection, dispense success/failure, and timeout events. Add shallow history on OutOfStock and guard [supplyAvailable] on dispense.”
✅ Result: A model that handles real-world failures gracefully.
📌 Use Case: Great for IoT, hardware-software integration, and prototyping.
6. How Visual Paradigm’s AI State Machine Diagram Generator Works (2026)
Visual Paradigm’s AI State Machine Diagram Generator is a game-changer for developers, architects, and product teams.
🔹 How It Works (Step-by-Step)
-
Access the Tool
-
Desktop:
Tools > AI Diagram > State Machine Diagram -
Online:
AI > State Machine Generator -
Chatbot: chat.visual-paradigm.com
-
-
Enter a Natural Language Prompt
“Generate a State Machine for a user login system with states: Logged Out, Logging In, Logged In, Locked Out. Events: clickLogin, invalidPassword, timeout. Add guard: [attempts < 3] on login failure. Add entry action: logLoginAttempt() on Logging In.”
-
Add Enhancements (Optional)
-
“Use orthogonal regions”
-
“Add shallow history on Locked Out”
-
“Include exit action: clearSession()”
-
-
Click Generate
✅ Boom! A fully editable, UML 2.5-compliant diagram appears in seconds. -
Edit & Export
-
Drag and reposition states
-
Add stereotypes (
<<businessRule>>,<<security>>) -
Link to class or sequence diagrams
-
Export to code (Java, Python, C++, C#)
-
Export to SCXML (for embedded systems)
-
💡 Pro Tip: Use the AI Chatbot for iterative refinement. Ask:
“Add a ‘Reset’ transition from any state to Logged Out.”
→ The AI updates the diagram instantly.
7. Benefits of AI-Powered State Modeling (Why It’s a Game-Changer)
| Benefit | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Speed | Generate a full diagram in under 1 minute |
| Accuracy | AI ensures UML 2.5 compliance — no invalid pseudostates or syntax errors |
| Error Detection | AI flags unreachable states, missing guards, or dead ends |
| Learning Curve | Beginners can model complex systems without mastering UML syntax |
| Collaboration | Share diagrams via cloud, version control, or team dashboards |
| Code Generation | Export directly to Java, Python, C++, or SCXML — no manual coding |
| Iterative Refinement | Ask the AI to “Simplify this state machine” or “Optimize layout” |
| Integration | Works with class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and CI/CD pipelines |
✅ The AI isn’t just a tool — it’s a co-designer.
8. Best Practices & Common Pitfalls to Avoid
✅ Best Practices
-
Start simple → add complexity later
-
Use domain-specific language (e.g., “Order”, “PaymentProcessor”)
-
Validate with: “Check for unreachable states”
-
Use shallow/deep history for user sessions or workflows
-
Link to class diagrams for traceability
-
Use orthogonal regions for concurrent behaviors
❌ Common Pitfalls
-
❌ Overcomplicating early — start with core states
-
❌ Missing guards — leads to invalid transitions
-
❌ Forgetting entry/exit actions — critical for logging, cleanup
-
❌ Ignoring unreachable states — can cause bugs in production
-
❌ Not validating — always ask the AI to check for issues
9. Resources & Tools (All Embedded Links)
Here are the best free resources to learn and use UML State Machine Diagrams in 2026:
-
📘 What is a State Machine Diagram? A Comprehensive UML Guide
→ Clear explanation of purpose, components, and real-world use. -
📘 State Diagram Quick Tutorial: Master UML State Machines in Minutes
→ Beginner-friendly walkthrough with visuals. -
📘 Interactive State Machine Diagram Tool
→ Create and edit diagrams in real time using AI. -
📘 UML State Machine Diagram Tutorial and Syntax Guide
→ Learn notation, composite states, and history. -
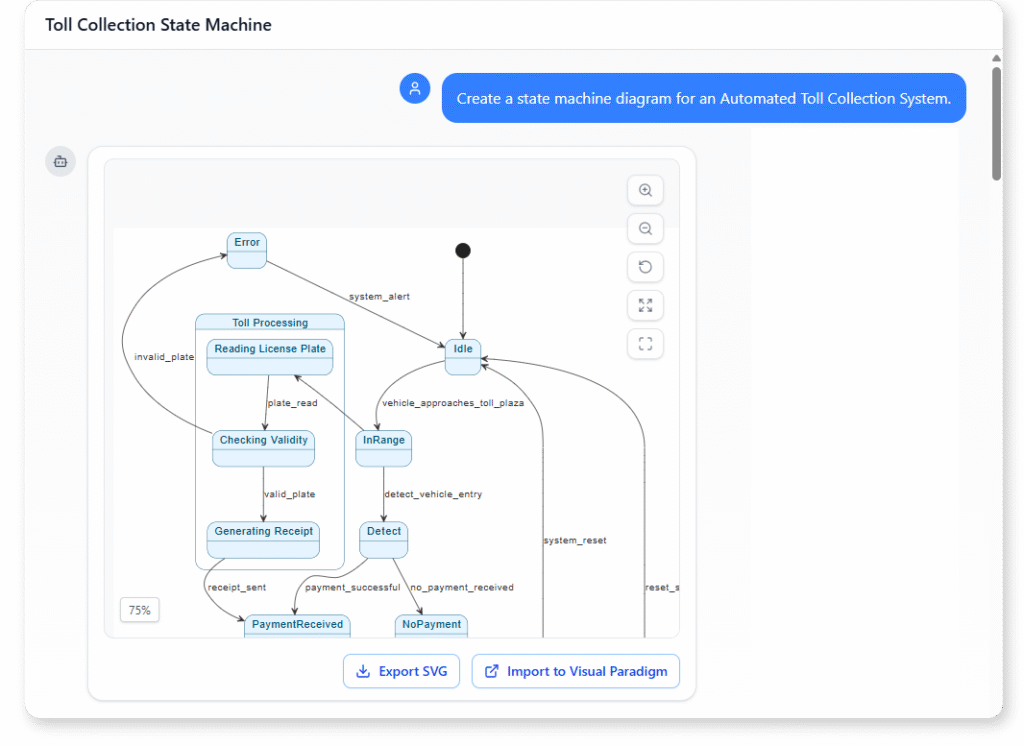
📘 Mastering State Diagrams with Visual Paradigm AI: A Guide for Automated Toll Systems
→ Real-world case study — great for inspiration. -
📘 Generating Source Code from State Machines in Visual Paradigm
→ Turn your diagram into Java, Python, or C++ code. -
📘 Visual Paradigm – UML State Machine Diagram Tool
→ Feature-rich online tool for developers and architects. -
📘 3D Printer State Machine: A Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide
→ Detailed walkthrough of state machine logic in hardware systems.
10. Conclusion: Why State Machines Are Essential in Modern Development
In 2026, state machines are not optional — they’re foundational.
Whether you’re building:
-
A microservice that processes payments,
-
An IoT device that responds to sensors,
-
A web app with complex user flows,
-
Or a robotic system with safety-critical logic,
…you need to model behavior clearly and consistently.
Visual Paradigm’s AI State Machine Diagram Generator removes the friction — turning natural language into professional, production-ready diagrams in seconds.
🚀 Your next step?
Go to chat.visual-paradigm.com → type:
“Generate a State Machine for a user login system with login, lockout, and logout.”
→ Watch the AI build it for you.
Final Word: Build with Clarity, Code with Confidence
You now have:
-
A solid understanding of state machine fundamentals
-
Real-world examples and use cases
-
A step-by-step method to create diagrams
-
Access to AI-powered tools that do the heavy lifting
✅ You’re not just learning UML — you’re learning to design better systems.
Start small. Use the AI. Iterate. Build with confidence.
🌐 Begin your journey today: chat.visual-paradigm.com
✅ This guide is designed for developers, architects, product managers, and beginners. All examples, tools, and links are up-to-date for 2026. No jargon. No fluff. Just real, actionable knowledge.












